2025 Annual Report of Metabolism and Target Organ Damage
The year 2025 marked an important stage in the continued development of Metabolism and Target Organ Damage (M&TOD; ISSN 2769-6375). Throughout the year, the journal remained committed to its core mission of publishing rigorous, peer-reviewed research that advances understanding of metabolic disorders and their effects on target organs. By steadily strengthening editorial standards, expanding international participation, and promoting academic exchange, M&TOD continued to build a solid foundation as a young international open access journal.
Highlights
- Indexing and metrics: M&TOD received its first Impact Factor (IF, 3.9) in June 2025 [Journal Citation Reports (JCR), Q2]. CiteScore increased from 3.0 (2023) to 3.4 (2024).
- Editorial leadership: Prof. Youfei Guan was appointed Co-Editor-in-Chief, contributing extensive expertise in renal, metabolic, and cardiovascular physiology and related diseases, along with strong academic leadership.
- Submissions and publications: M&TOD received 236 submissions and published 65 articles in 2025. The rejection rate increased to 78%, reflecting the journal's commitment to rigorous peer review and publication quality. Original Articles and Reviews together accounted for over 84% of published content.
- International authorship: From 2021 to 2025, authors represented a broad range of countries. The largest contributions came from China (32%), Italy (18%), and the United States (16%), with other countries collectively accounting for 34%.
- Citations and visibility: In 2025, citations reached 300 in Web of Science and 405 in Google Scholar, continuing a clear upward trend.
- Special Issues: 15 Special Issues were launched in 2025, covering diverse topics in metabolism and target organ damage, including obesity, steatotic liver disease, type 2 diabetes, and Wilson's disease.
- Editorial Board updates: 13 new members joined the Editorial Board, bringing the total to 82 members from 15 countries. Among them, 59 were included in the World's Top 2% of Scientists (Stanford University-Elsevier list), and 3 were named Highly Cited Researchers 2025 by Clarivate Analytics.
- Webinars and academic engagement: M&TOD organized 14 webinars with a cumulative online audience of nearly 180,000 viewers and participated in multiple academic conferences to enhance visibility and scholarly exchange.
- Interviews: 6 interviews with leading international experts were conducted, further strengthening engagement with the global research community.
1. Indexing and Metrics
The journal received its first IF (3.9) in June 2025, ranking in the second quartile (Q2) of Endocrinology & Metabolism and within the top 30% of journals in this category. CiteScore increased from 3.0 (2023) to 3.4 (2024), placing the journal in the third quartile of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism.

Figure 1. Impact Factor and CiteScoreTracker of M&TOD
2. Editorial Leadership Update

Prof. Youfei Guan
Advanced Institute for Medical Sciences, Dalian Medical University, Dalian, Liaoning, China
In 2025, Prof. Guan Youfei was appointed as Co-Editor-in-Chief of M&TOD. Prof. Guan is a distinguished expert in renal, metabolic, and cardiovascular physiology and diseases. He is a Distinguished Professor under the Changjiang Scholars Program of the Ministry of Education of China and a recipient of the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars. He has been recognized as a Highly Cited Researcher in Medicine in China for nine consecutive years. His appointment strengthens the journal's academic leadership and strategic development.
3. Submissions and Publications
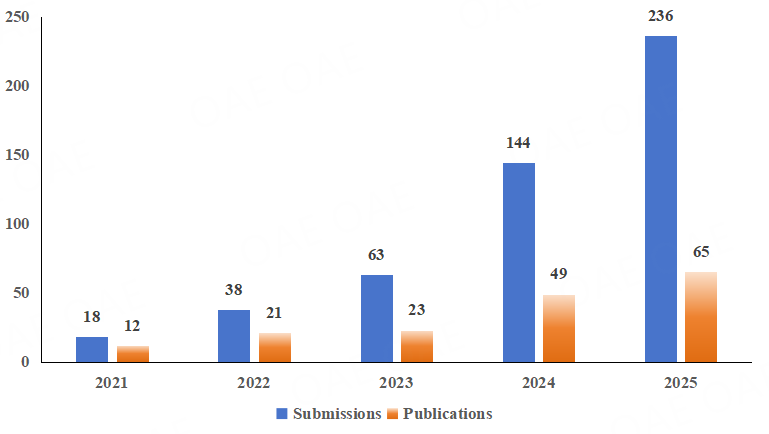
Figure 2. Submissions and Publications (2021-2025)
Compared with 2024, M&TOD experienced notable growth in 2025. Annual submissions increased from 144 to 236 (a 64% increase), while publications rose from 49 to 65 (a 33% increase).
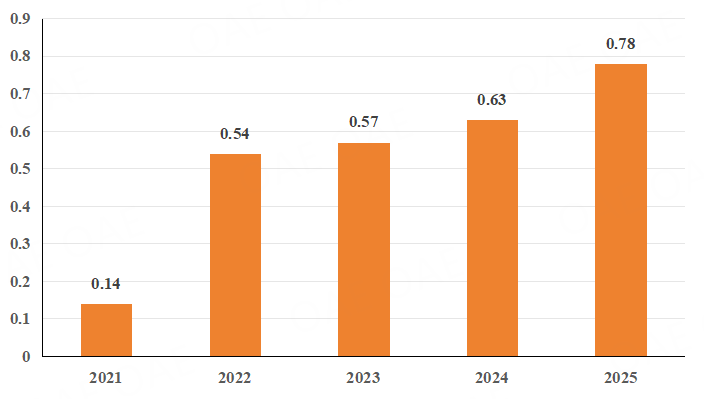
Figure 3. Rejection Rate (2021-2025)
From 2021 to 2025, the rejection rate increased steadily from 14% to 78%, reflecting progressively stricter peer-review standards and a stronger emphasis on publication quality.
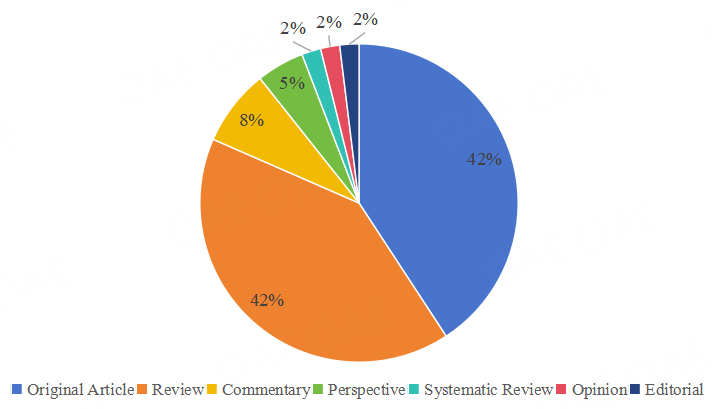
Figure 4. Article Type Distribution (2025)
In 2025, Original Articles (42%) and Reviews (42%) constituted the majority of published content, together accounting for over 84% of all articles. The remaining articles included Commentaries, Perspectives, Systematic Reviews, Opinions, and Editorials, ensuring diversity in article formats while maintaining a strong research focus.
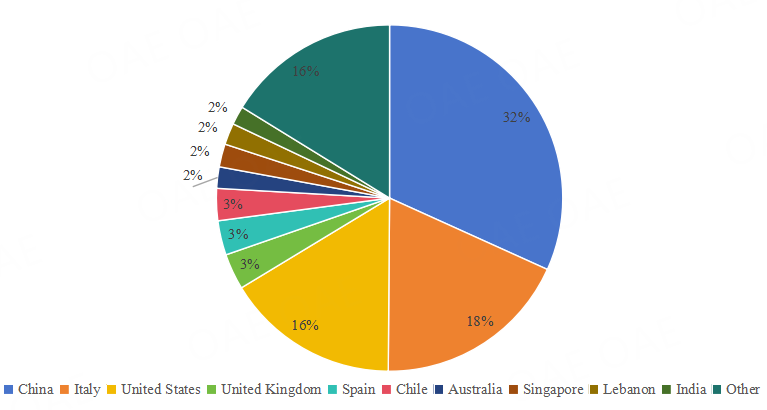
Figure 5. Geographic Distribution of Authors (2021-2025)
Between 2021 and 2025, authors originated from a wide range of countries/regions. The largest proportion came from China (32%), followed by Italy (18%) and the United States (16%). Additional contributions were from the United Kingdom, Spain, and Chile (3% each), as well as Australia, Singapore, Lebanon, and India (2% each). Authors from other countries collectively accounted for 16% of the total. This distribution highlights a strong international contribution, with a particular concentration in China, Italy, and the United States.
4. Citations and Readership
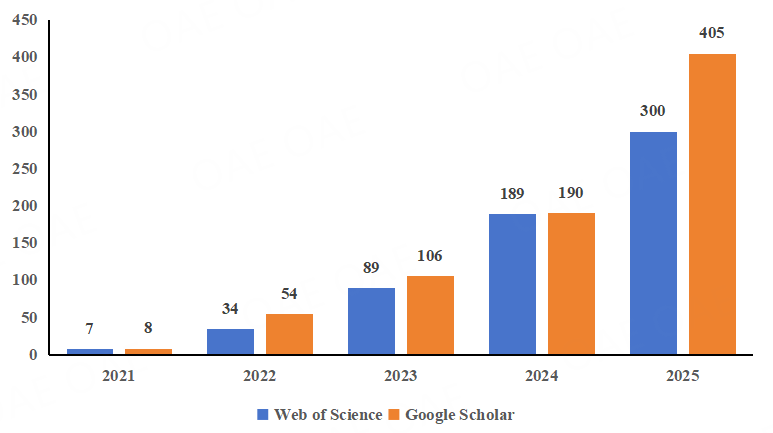
Figure 6. Citations (2021-2025)
Citations increased substantially in 2025. Web of Science citations rose from 189 to 300, while in Google Scholar citations increased from 190 to 405, reflecting growing academic visibility and readership.
Table 1. Top 10 Most-Read Articles in 2025
The top 10 most-read articles in 2025 accumulated 1,041-2,246 views each, with a strong focus on steatotic liver disease, metabolic disorders, and the application of artificial intelligence in diagnosis and management. These readership patterns highlight areas of sustained interest within the journal's scope.
5. Special Issues
In 2025, M&TOD launched 15 Special Issues addressing key topics in metabolism and related disorders, such as women leading metabolic sciences, obesity and its complications, childhood obesity, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, Wilson's disease, type 2 diabetes, and diabetic cardiovascular disease. Each issue was led by distinguished Guest Editors with recognized expertise, supporting focused discussion and dissemination of emerging research.
Table 2. Special Issues Published in 2025 (Partial List)
| Cover | Topic | Guest Editors |
|---|---|---|
 | Women Leading Metabolic Sciences | Sonia Michael Najjar; Ilaria Barchetta |
 | Obesity and Its Associated Metabolic Disorders: Insights Across Organ Systems | Qiang Li |
 | Metabolic Heterogeneity in Childhood Obesity and Preventive Strategy | Yi Song |
 | MetALD: Opportunities and Challenges | Ashwani K. Singal; Robert J Wong |
 | Wilson's Disease: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Management | Jiangao Fan; Jianshe Wang; Yiwen Shi |
 | Exploring Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications | Hui Tian; Hongzhou Liu |
 | OAE 10th Anniversary Commemorative Special Issue: Metabolic Dysfunction and Target Organ Damage --- Emerging Insights and Future Perspectives | Amedeo Lonardo |
 | New Insights in MAFLD | Mohammed Eslam; Ziyan Pan |
 | Emerging Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies in Diabetic Cardiovascular Disease | Yong Xu; Shiwei Liu |
6. Editorial Board Updates
In 2025, 13 new members joined the Editorial Board, bringing the total to 82 members representing 15 countries, with major representation from China, Italy, United States. Among them, 59 have been recognized in the World's Top 2% of Scientists (Stanford University-Elsevier list) for 2025, and 3 have been named Highly Cited Researchers 2025 by Clarivate Analytics.
Table 3. Editorial Board Members Appointed in 2025
| Photo | Name | Institution |
|---|---|---|
 | Jean-François Dufour | Centre for Digestive Diseases, Lausanne, Switzerland |
 | Jiangao Fan | Xinhua Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China |
 | Maite G. Fernández‐barrena | University of Navarra, Pamplona, Spain |
 | Xianghui Fu | Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China |
 | Lynn H. Gerber | George Mason University, Fairfax, Virginia, USA |
 | Francesco Giorgino | University of Bari Aldo Moro, Bari, Italy |
 | Qiuhe Ji | Northwest University Affiliated Xi'an International Medical Center Hospital, Xi'an, Shaanxi, China |
 | Kusum K. Kharbanda | Veterans' Affairs Medical Center, Omaha, Nebraska, USA |
 | JianJun Li | Fuwai Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, China |
 | Marcello Persico | University of Salerno, Baronissi, Italy |
 | Feng Sun | Peking University, Beijing, China |
 | Wei Wu | Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China |
 | Jichun Yang | Peking University Health Science Center, Beijing, China |

Figure 7. Distribution of Editorial Board Members by Country/Region
7. Webinars
In 2025, M&TOD organized 14 webinars, attracting nearly 180,000 online viewers. Ten webinars were held as part of the 10th Anniversary of OAE Publishing, the publisher of M&TOD. Topics included metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), emerging therapies, and metabolic stress across organ systems. These events facilitated academic exchange across research, clinical practice, guidelines, and public health perspectives.




Figure 8. Online Academic Events in 2025
Table 4. OAE 10th Anniversary Webinar Series of M&TOD in 2025
| Topic | Date | Chair/Moderator(s) | Speaker(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HSD17B13: A New Therapeutic Target for Fatty Liver Disease | October 19 | Alani Luo | Prof. Youfei Guan |
| Sex Differences in MASLD | October 20 | Tilda Li | Amedeo Lonardo |
| How to Think MASLD-HCC Management Progressively? | October 21 | Tilda Li/Amedeo Lonardo | Jean-François Dufour |
| Obesity Attenuates Cardiovascular Protection | October 21 | Tilda Li/Amedeo Lonardo | Lilach O. Lerman |
| Novel Agents to Treat MASLD | October 21 | Alani Luo | Minghua Zheng |
| Chinese Guidelines for MAFLD 2025 | October 22 | Alani Luo | Jiangao Fan |
| MASLD as a Multisystem Disease? | October 22 | Tilda Li/Amedeo Lonardo | Christopher D Byrne |
| Lactate Shuttle in Glucose Homeostasis | October 22 | Ling Xiao | Yan Chen |
| Clinical Precision Subtyping of MASLD | October 23 | Yujin Chi | Jin Chai |
| Public Policy and MAFLD | October 24 | Amedeo Lonardo | Jacob George |
8. Expert Interviews
In 2025, M&TOD conducted six interviews with internationally recognized experts from leading institutions in Italy, Switzerland, and China. These interviews provided insights into recent scientific advances and future research directions. Special acknowledgment is extended to Editor-in-Chief Prof. Amedeo Lonardo for his substantial contribution as a lead interviewer and for preparing several interview manuscripts.






Figure 9. Expert Interviews in 2025
9. Academic Conferences and Outreach
The Editorial Office of M&TOD actively participated in 11 major academic conferences across China in 2025, covering diabetes, obesity, endocrinology, and cardiovascular diseases. Through these activities, the journal strengthened connections with researchers and clinicians while enhancing visibility within relevant scientific communities.
Table 5. Academic Conferences Attended by the M&TOD Editorial Office in China (2025)
| No. | Conference Name | Date | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | China Advanced Technologies and Therapies for Diabetes and Obesity | March 28--30 | Shenzhen |
| 2 | The 20th Xiangya International Diabetes Immunology Forum | April 18--20 | Changsha |
| 3 | The 21st Peking University Diabetes Forum | May 23--25 | Beijing |
| 4 | Asia Pacific Alliance for Obesity and Sarcopenia Metabolism (APAOSM) 3rd Scientific Meeting | July 11--12 | Shenzhen |
| 5 | China Obesity Congress | August 15--17 | Beijing |
| 6 | The 22nd Annual Meeting of Chinese Society of Endocrinology | August 21--24 | Chongqing |
| 7 | The 27th Annual Conference of the Chinese Medical Association on Cardiovascular Diseases | September 18--21 | Xi'an |
| 8 | International Symposium of Lipid and Tissue Injury, ISLT 2025 | October 9--13 | Chongqing |
| 9 | The 27th Scientific Meeting of the Chinese Diabetes Society | November 19--22 | Xi'an |
| 10 | Annual Meeting of the Endocrinology Branch of Beijing Medical Association and Complex Case Discussion Session | December 13 | Beijing |
| 11 | The 2nd Academic Conference of the Diabetes Society, Sichuan Medical Association | December 25--27 | Chongqing |
10. Editorial Board Meetings
Under the leadership of Editors-in-Chief Prof. Amedeo Lonardo and Prof. Youfei Guan, M&TOD convened three Editorial Board meetings in 2025. Discussions focused on editorial policy, manuscript quality control, Special Issue planning, and long-term development strategies, supporting continuous improvement of journal operations.
Acknowledgments
Overall, 2025 represented a year of steady and constructive progress for M&TOD. With improved editorial selectivity, expanded international participation, growing citation activity, and enhanced indexing coverage, M&TOD continues to develop as a credible platform for research on metabolic disorders and their effects on target organs. We sincerely thank all Editorial Board members, guest editors, reviewers, authors, readers, and editorial staff for their dedication and support throughout 2025 and look forward to further strengthening the journal's academic contribution in the years ahead.
Editor: Alani Luo
Language Editor: Catherine Yang
Production Editor: Ting Xu
Respectfully Submitted by the Editorial Office of Metabolism and Target Organ Damage











