Volume 4 (2018) – 60 articles
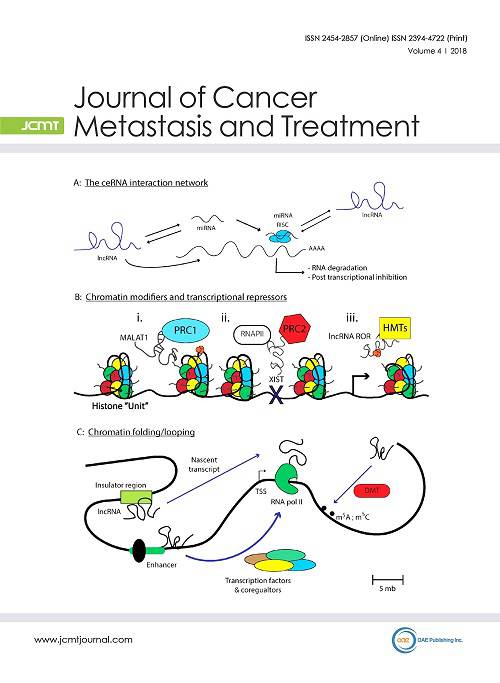
Cover Picture: Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNA) are a form of non-coding RNA, larger than 200 nucleotides in length that are not translated into a protein product. In 2005,the FANTOM3 project identified ~35,000 non-coding transcripts derived from ~10,000 distinct loci that produce non-coding RNA molecules that are 5’ capped, spliced, and poly-adenylated, yet have little or no open reading frame (ORF). Today, there are over 118,000 newly identified lncRNAs, many of which have little to no known biological function. The current hypothesis is that lncRNAs are important in dampening stochastic gene expression by modulating the epigenetic landscape of the genome. The classic example of which, being XIST—mediated gene silencing of the X-chromosome. Additionally, there is considerable evidence that lncRNAs regulate the physiological pathways required for the initiation and maintenance of cell proliferation, differentiation, tumorigenesis, as well as metastasis.
The cover picture, indicates the various modalities by which lncRNAs can interact with other non-coding RNAs so as to promote or inhibit the cellular phenotypes mentioned above.
view this paper The cover picture, indicates the various modalities by which lncRNAs can interact with other non-coding RNAs so as to promote or inhibit the cellular phenotypes mentioned above.
Read Online Viewed:
Download This Volume Viewed:








