Volume 5, Issue 2 (2025) – 12 articles
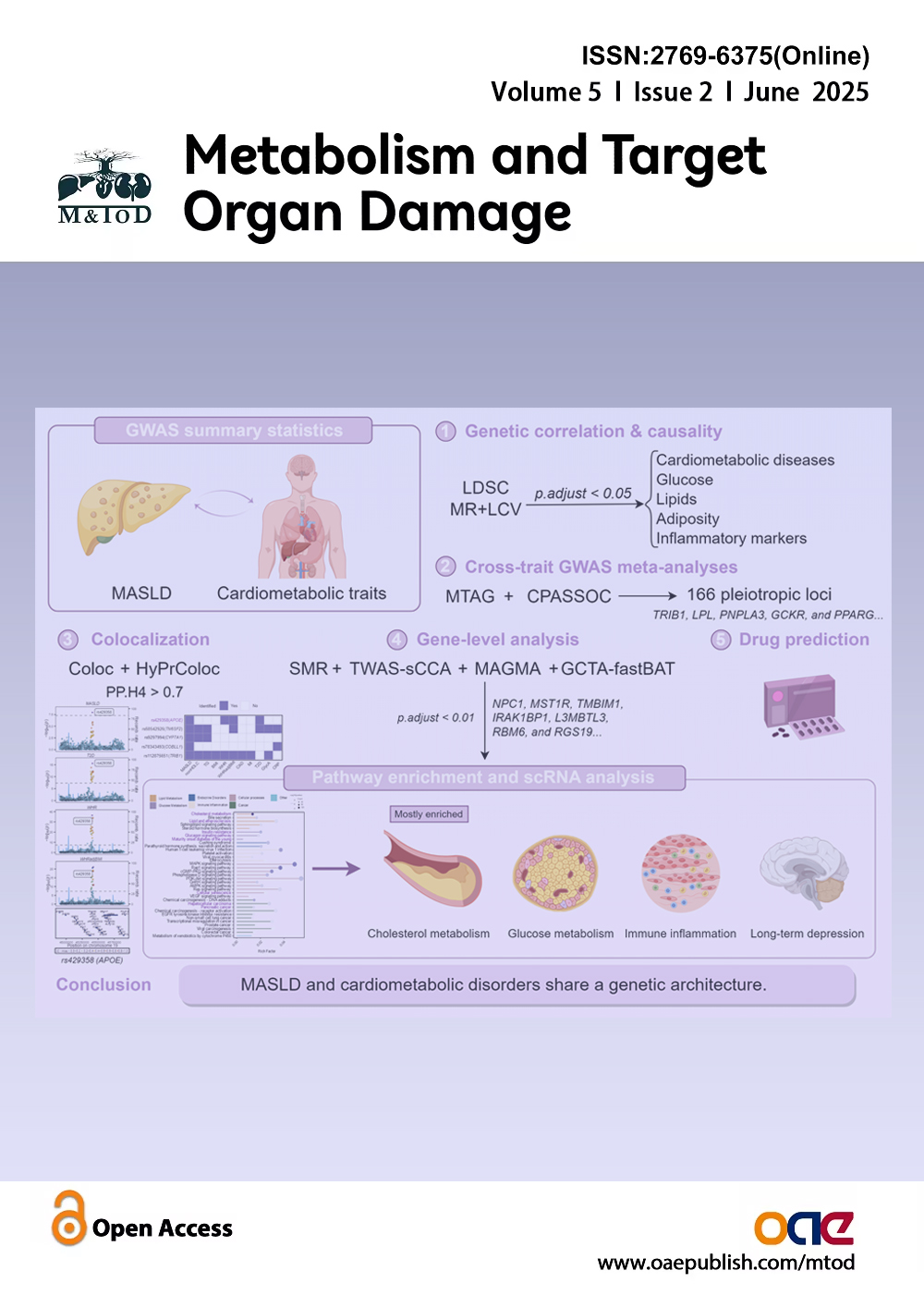
Cover Picture: This study provides a comprehensive multi-omics analysis revealing the shared genetic architecture between metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and cardiometabolic traits (CMTs). By integrating GWAS data with single-cell RNA sequencing, the authors identified 166 shared genetic loci, highlighted key genes such as APOE, LPL, and TRIB1, and uncovered common biological pathways—particularly those related to lipid and glucose metabolism, immune inflammation, and macrophage activity. The findings underscore the central role of cholesterol dysregulation in the liver-heart axis and offer novel insights into the mechanisms driving MASLD-CMT comorbidity, paving the way for personalized therapeutic strategies.
view this paper