Volume 3, Issue 4 (August, 2023) – 9 articles
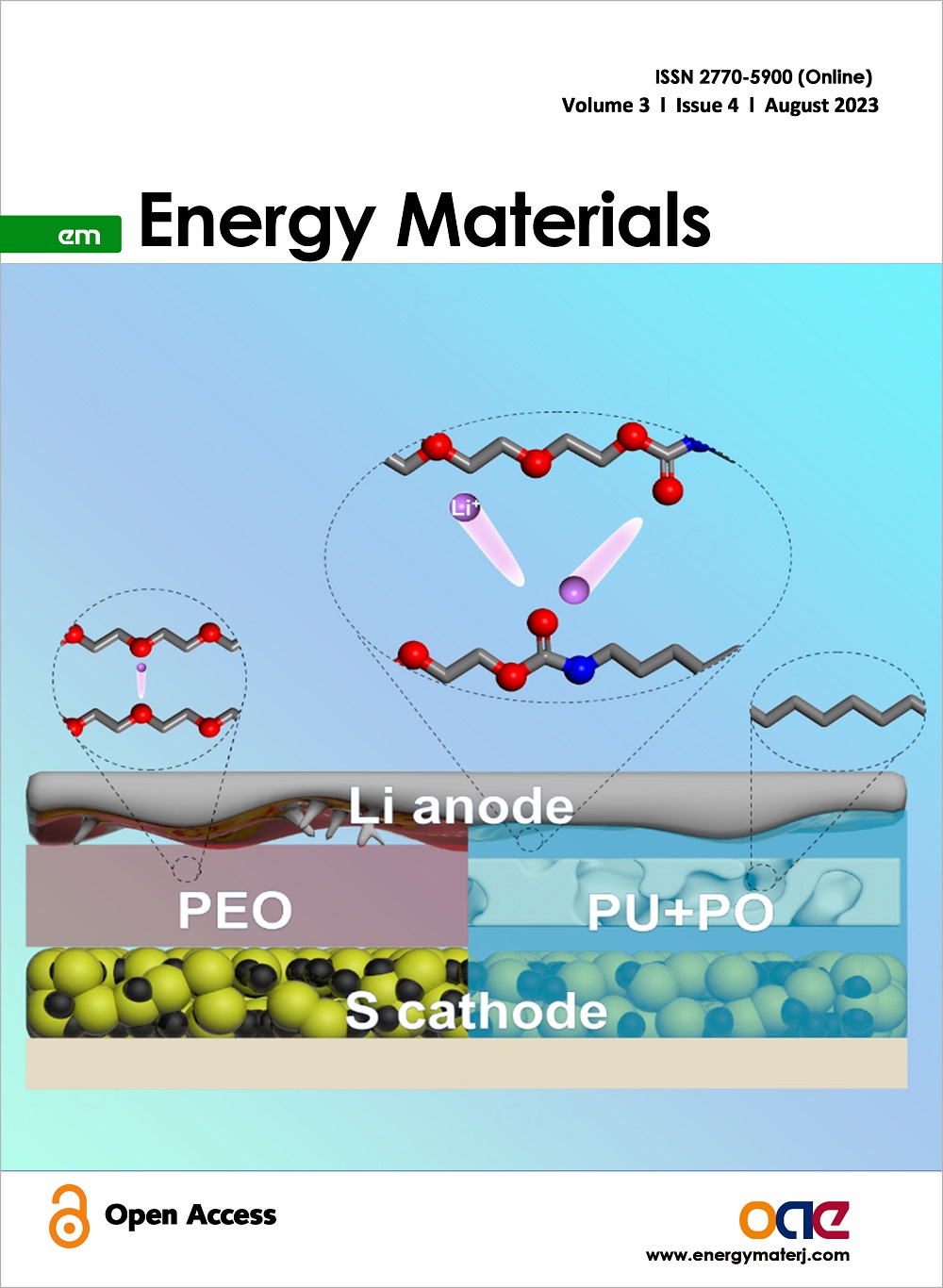
Cover Picture: Solid-state lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries are promising secondary batteries because of high energy density and high safety, but their practical application is severely hindered by poor Li+ transport in batteries due to low ionic conduction of the electrolyte and unstable electrode/electrolyte interface. This study address the issue by using an polyurethane-based electrolyte. The polar urethane/urea groups of electrolyte reduce the hopping energy barrier of lithium ions (Li+), which resulting in high ionic conductivity, high ion transference number and low activation energy. In addition, the polar urethane/urea groups endow the electrolyte with high adhesion, which allows the electrode/electrolyte interfaces to self-heal timely after being damaged during cycling. Self-healing of the electrode/electrolyte interfaces during cycling was in-situ observed by a laser confocal microscope. This study demonstrates the importance of polar groups in electrolytes in maintaining a fast and stable Li+ transport, which can be applied to other solid-state batteries.
view this paper