Volume 6 (2020) – 55 articles
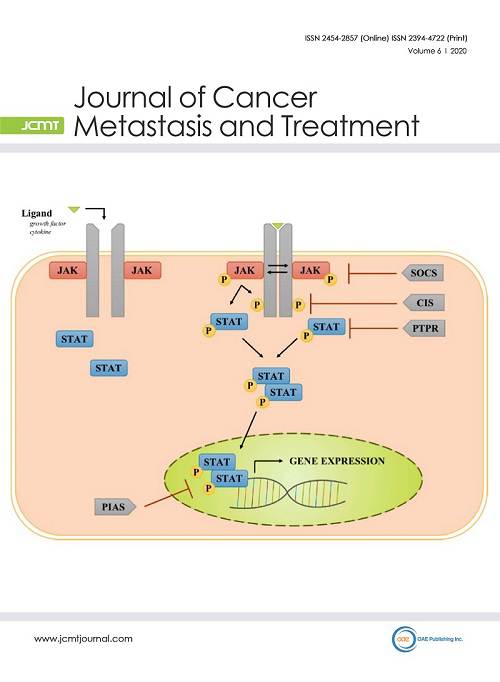
Cover Picture: The janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT) pathway mediates cytokine and growth factor signaling. These ligands bind to their respective transmembrane receptor subunits which results in multimerization of subunits, bringing receptor-associated JAKs in close proximity to each other. JAKs then activate each other via transphosphorylation. Activated JAKs phosphorylate the cytoplasmic domain of the cytokine receptor to provide a docking site for STATs. Once STATs bind to this site, they are phosphorylated and activated by JAKs. Phosphorylated STATs homo- or hetero-dimerize and translocate to the nucleus, where they act as transcription factors for genes promoting cell proliferation, survival, invasion, and migration. The JAK/STAT pathway is regulated by suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) family of proteins, which includes the cytokine-inducible SH2-conaining protein (CIS). Protein inhibitor of activated STAT (PIAS) proteins and protein tyrosine phosphatase receptors (PTPRs) are other negative regulators of this pathway. STAT hyperactivation, through mechanisms such as increased cytokine signaling, activating mutations, and hypermethylation of negative regulators, has been implicated in a variety of hematological and solid tumor malignancies. Therefore, components of this pathway are potential targets for cancer therapy.
view this paper
Read Online Viewed:
Download This Volume Viewed:




