Volume 2, Issue 4 (December, 2022) – 5 articles
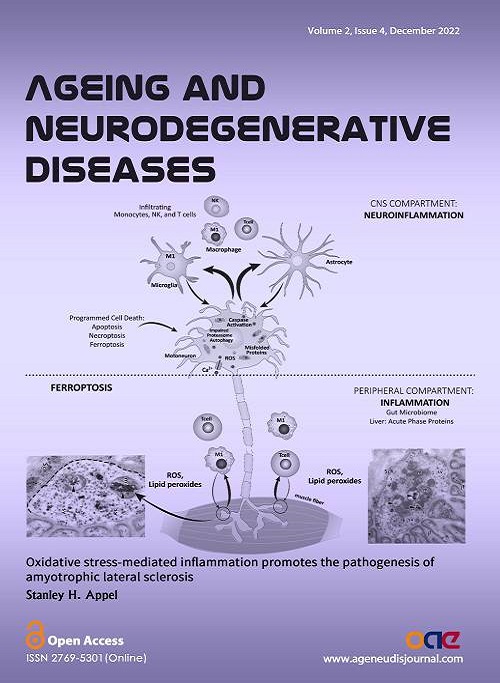
Cover Picture: Neuroinflammation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is characterized by activation of monocytes/macrophages and T lymphocytes in the periphery and microglia and astrocytes within the central nervous system. This review emphasizes the role of oxidative stress in promoting systemic inflammation and the early stages of neurodegeneration. Motor axon terminals of ALS patients have significantly increased intraluminal calcium and dysfunctional mitochondria, increasing the formation of lipid peroxides and ferroptosis programmed cell death. Serum lipid peroxides and acute phase proteins are elevated, and regulatory T lymphocytes (Tregs) are dysfunctional, impairing immune-mediated neuroprotection. Macrophages are pro-inflammatory; the expression of genes involved in inflammation is increased in peripheral monocytes/macrophages of ALS patients. Suppressing these multiple components of inflammation is an important therapeutic goal and provides an opportunity to interrupt the self-propagating cytotoxic cycle. Two clinical trials with autologous infusions of ex vivo expanded Tregs have been safe and well tolerated, with promising.
view this paper
Download This Issue Viewed: